Not all programs can run in the same environment, different environments are needed for different programs to run. Therefore, Windows makes sure all programs get the environment they need, and to provide this environment Windows tries to know the environment requirements for a program. Furthermore, it stores this information so that it can be retrieved. All this is made possible by Environment Variables. In simple words, Environment Variables on Windows 10 is a data storing mechanism.
Unable to comprehend it properly? No worries. In this post, we will understand more about Environment Variables, how they work, how to create them, edit and delete environment variables.
What Are Environment Variables in Windows 10?
Environment variables are dynamic variables that save data corresponding to creating different environments for various processes and programs.
To understand Environment Variables on Windows 10, let us take an example. Before that, keep one thing in mind, for a program to use a tool, the location of the tool is required. This helps access it. In addition to this, the program needs to know whether it has permission to use the tool or not. Once all this is identified the program then accesses the information by asking Windows. After that, Windows checks Environment Variables (EVs) for the data followed by creating an environment in which the said program can run.
In simple terms, Environment Variables save data accessible to each process and program running on the system for all users. The data stored by these variables helps programs run in the environment they were designed for.
Some of the most important EVs on Windows include USERNAME, PATH, AND HOMEPATH. All of them have the values that a process and user can access without any restriction. For example, the HOMEPATH environment variable has the location of programs stored on the system. This means whenever Windows wants to know the location of the installed programs it can use this variable.
Also Read: Fix – Windows 10 Update Failed To Install
How to Set Environment Variables in Windows 10?
To set Environment Variable, you need to either log in as admin or have administrative rights. In case you don’t have admin rights, you can ask the system administrator for the same.
Once you have admin privileges move ahead and set Environment Variables:
1. In the Windows search bar, type Advanced system settings.
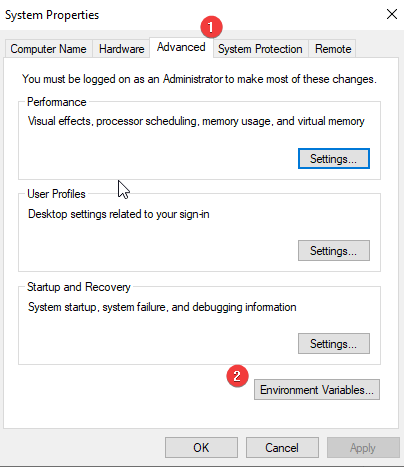
2. Click the Advanced tab > box, double click Environment Variables.
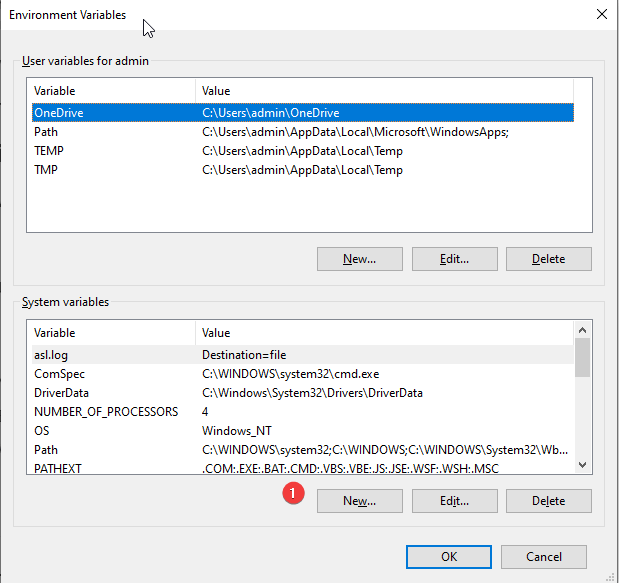
3. In the new window that opens, you will see 2 types of variables. To change EVs for the current user only make changes under User variables. However, if you want to apply it system-wide make the changes under System variables.
Say, for example, you have installed Java and want to add its path to the Environment Variable, you need to follow these steps:
1. Under System variable click New
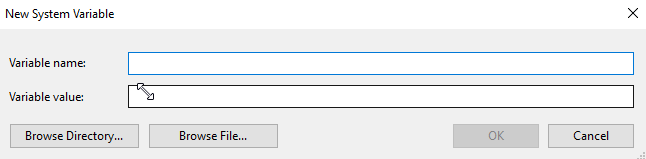
2. You will now see the New User Variable Here, enter JAVA_HOME in the Variable name field followed by clicking the Browse Directory button and navigating to the location where Java is installed this will help key in the entry for Variable value.
3. Once done, press OK this will add the JAVA_HOME variable to the PATH variable.
Now that we have added the variable if you want you can edit that variable. To do so, follow these steps.
How to Edit Environment Variables
To edit any environment variables, select variables from the list > Edit. You will now see the Edit environment variable panel, from here you can create, delete, and edit variables.
Select the one you want to alter > Edit. Change variable value as per your liking. In the same way, you can remove the EV too.
What Is the Windows PATH Variable and How Can I Change it?
Wondering what is PATH variable, well it is the address book of commands and programs. Generally, when you run a program via the command line the path you enter is the PATH variable.
Note: Only the programs that can be used via the command line have PATH variables. This means programs designed to be used via Graphical User Interface don’t have their addresses in the PATH variable.
How does the process work?
When the user enters a command in the command line. Windows looks up for the address in the current directory. In case, there’s nothing found in the current directory the OS looks up the PATH variable to find the address.
To enter an address in the PATH variable, go to Advanced System Settings > Environment Variable > double click it > hit the PATH variable, and click Edit.
Here, add, remove, and edit directories.
The PATH variable varies from user to user. This means different users can list different directories without changing the variable for every user. With that said, to make the tool used by every user, you need to edit the PATH variable under the System Variables.
What are Environment Variables in the Windows 10 Store?
Nothing can work without data, the same is true for programs. Hence, to ensure data is accurately available. Windows stores this essential data in global variables popularly known as Environment Variables.
These Environment variables can be set, edited, and removed from the Advanced System Settings panel.
Also note, each user on your machine will have different Environment Variables under User variables. While system EVs will be the same for all. However, you need admin privileges to edit or delete them.
In simple words, Environment Variables are a way to save important data required to run processes and programs. Therefore, when creating or modifying any EV make sure you know what you are doing, as an incorrect action might make you lose data. We hope you find the information helpful and can understand what EVs are and their role on Windows. In case you have any questions do let us know in the comments section below.



Leave a Reply