It has just been a couple of years since most countries upgraded their mobile connections to 5G, and we have 6G in the trial phase, with features being highlighted every month or so. Many countries have adopted 5G only in major cities, and others are still on the 4G network.
I do not know what the rush is about, but upgrading my SIM card every two years for a newer “G” would be an unnecessary enforced expense. In my personal opinion, researchers and telecommunications authorities should stop the iPhone upgrading method (“by introducing negligible changes every year in the newer model”) and make significant changes so that the new technology lasts for a decade or so.
What Is 5G And What Are Its Features?

5G stands for fifth-generation wireless technology, the latest standard for mobile networks. It is designed to offer significantly faster data speeds, lower latency (or delay), and more reliable connections compared to previous generations, like 4G.
Here are some key features of 5G:
Faster Speeds – 5G can offer speeds up to 100 times faster than 4G. This means downloading large files, streaming high-definition videos, and using bandwidth-intensive applications will be much quicker.
Lower Latency – Latency refers to the delay between sending and receiving data. 5G can reduce latency to as low as 1 millisecond, a major improvement over 4G’s latency of around 30 milliseconds.
Greater Capacity – 5G networks can handle a much larger number of devices simultaneously. This is crucial as more devices become connected through the Internet of Things (IoT), including smart homes, wearables, and industrial machines.
Improved Reliability – 5G is designed to be more reliable, even in crowded or remote areas, ensuring that devices maintain strong connections even under heavy network traffic.
Support for New Technologies – 5G is expected to play a crucial role in the advancement of emerging technologies like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR).
The global roll-out of 5G is ongoing, with many cities and countries gradually upgrading their infrastructure to support it.
Read Also: iOS 18.2 Beta 3: Apple Intelligence And Other Features You Can Test Right Now
What Is 6G And What Are Its Features?

6G (sixth generation) is the anticipated next evolution of wireless technology, expected to follow 5G and revolutionize how we connect, communicate, and interact with technology.
While 6G is still in the early stages of development and research, it promises to build on the advancements made by 5G and introduce even more transformative capabilities. Here’s an overview of what 6G could offer:
- Faster Speeds
6G is expected to deliver data speeds that are 100 times faster than 5G. While 5G can reach speeds of up to 10 Gbps (gigabits per second), 6G could push speeds up to 100 Gbps or even higher.
- Ultra-Low Latency
The latency, or the delay in data transmission, will be further reduced in 6G, potentially achieving sub-millisecond latency (less than 1 millisecond). This would make real-time applications—such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), telemedicine, and remote control of machines—almost indistinguishable from interacting with physical reality.
- Terahertz Frequencies
6G will likely operate in the terahertz (THz) frequency range, which is above the millimeter waves used by 5G. These higher frequencies offer extremely high data transfer rates and can provide more bandwidth.
- AI-Powered Networks
Artificial Intelligence (AI) will play a central role in 6G networks, with AI being used for network optimization, traffic management, security, and automation.
- Integrated Smart Devices
6G will enable the hyper-connected world, where not only smartphones and laptops but also everyday objects (e.g., clothing, vehicles, appliances) are seamlessly connected to the network.
- Advanced Holograms and XR
Extended Reality (XR), which encompasses virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), will see dramatic advancements in 6G. We could see 3D holographic communication in real-time, where people can interact with life-like holograms for video calls, meetings, entertainment, and education.
- Autonomous Systems
The ultra-fast speeds and low latency of 6G will enable further advancements in autonomous systems, including self-driving cars, drones, and robotics.
These systems will need near-instantaneous communication to make split-second decisions, and 6G could provide the infrastructure for that, allowing vehicles to communicate with each other and with infrastructure to avoid accidents and optimize traffic flow.
- Global Coverage
6G aims to provide global coverage that will include remote areas like rural regions, oceans, and even space.
- Security and Privacy
With the increased interconnectivity and vast amount of data being transmitted in 6G networks, security will be a critical concern. Quantum encryption and other advanced security technologies will likely be integrated into 6G to protect data and communications from hacking and unauthorized access.
- Sustainability
6G networks will be designed with energy efficiency in mind, aiming to reduce the carbon footprint of wireless technologies. With the increasing demand for data and devices, ensuring that 6G can operate sustainably, optimizing power usage, and minimizing waste.
6G is still in the research and early development phases, and it’s expected to start rolling out around 2030. By then, technologies like AI, edge computing, and quantum computing could be far more mature, helping make 6G a reality.
Significant Differences Between 5G and 6G Networks

While 5G and 6G are both part of the next generations of mobile wireless technology, 6G will significantly surpass 5G in several key areas. Here are the most notable differences:
- Speed
- 5G: Offers speeds up to 10 Gbps (gigabits per second), which is already a massive improvement over 4G.
- 6G: Expected to deliver 100 Gbps or more, which means up to 100 times faster than 5G. This would enable near-instantaneous downloads and uploads, even of ultra-large files (e.g., 16K videos or massive datasets).
- Latency
- 5G: Has latency as low as 1 millisecond, making it suitable for real-time applications like gaming and remote surgeries.
- 6G: Will reduce latency to sub-millisecond levels, potentially as low as 0.1 milliseconds. This will enable near-instantaneous communication for applications such as autonomous systems and holographic communication.
- Network Architecture
- 5G: Uses a mix of sub-6 GHz and millimeter-wave frequencies to provide faster speeds and lower latency. It also uses network slicing to cater to different use cases.
- 6G: Expected to use terahertz frequencies (above 100 GHz), which offer even greater bandwidth but require more advanced antenna technology and new signal processing techniques. It will also integrate more advanced AI-driven networks for real-time optimization and management.
- Device Density and Connectivity
- 5G: Designed to support 1 million devices per square kilometer, which is crucial for the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart cities.
- 6G: Will support even more dense connectivity, enabling hyper-connectivity where every object—including humans, machines, and environments—can communicate seamlessly. It will also support 6G networks in space, such as low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
- User Experience
- 5G: Brings improvements in AR/VR, high-definition video streaming, and autonomous vehicles, among other applications. The experience is significantly better than 4G in terms of speed, coverage, and reliability.
- 6G: Will offer ultra-immersive experiences, such as holographic communications, 3D/360-degree video streaming, and true mixed-reality environments. The user experience will feel much more seamless and life-like, with AI and extended reality (XR) technologies integrated into everyday life.
- AI and Automation
- 5G: Includes AI to optimize network operations, traffic management, and quality of service, but it is still mostly human-driven in terms of decision-making.
- 6G: Will be heavily AI-driven with autonomous network management, predictive analytics, and self-healing networks. AI will enable near real-time decision-making for dynamic network optimization and user experience personalization.
- Global Coverage
- 5G: Still reliant on terrestrial towers, and while it expands coverage, some remote and rural areas remain underserved.
- 6G: Will offer global coverage, including remote regions, oceans, and even space. This could be achieved by combining terrestrial networks with satellite constellations and airborne networks (e.g., drones).
- Quantum Computing and Security
- 5G: Incorporates advanced encryption and security features to safeguard data and user privacy, but still relies on traditional computing methods for encryption.
- 6G: Will likely integrate quantum computing to provide ultra-secure communication and quantum encryption for protecting sensitive data, which will be crucial as the volume and complexity of data grow.
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- 5G: Although more energy-efficient than 4G, 5G still requires significant energy consumption to support its high-speed data transfers and massive infrastructure.
- 6G: Will be designed with a focus on sustainability, aiming to reduce carbon footprints and energy consumption through green technologies like AI-based energy optimization and low-energy hardware.
- Use Cases and Applications
- 5G: Primarily targets industries like smart cities, healthcare, transportation, gaming, and entertainment, with the ability to enable things like autonomous driving, telemedicine, and remote work.
- 6G: Will go beyond current applications to support advanced use cases like holographic communication, autonomous robots, digital twins, and space exploration. It will enable AI-powered ecosystems where devices not only communicate but also think and make decisions autonomously.
Read Also: How To Convert XAPK to APK?
What Are The Benefits Of A 5G Transformation To 6G In The Near Future?
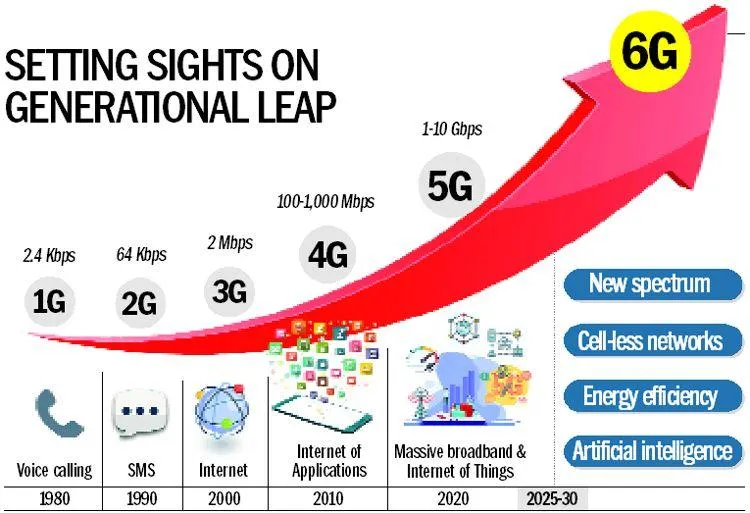
The shift from 5G to 6G won’t happen overnight; it will require substantial progress in technology, infrastructure, and regulatory frameworks. However, the potential rewards are vast:
Transforming Industries – From healthcare to transportation, 6G has the potential to revolutionize a variety of sectors by enabling new applications and services that demand ultra-fast, reliable, and low-latency communication.
Improved User Experience – Consumers can look forward to even more immersive and seamless experiences, from augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to smart cities and interconnected homes.
Boosting Economic Growth – The rollout of 6G could spur economic expansion by opening up new business opportunities, creating jobs, and tapping into emerging markets.
Which Companies Are Working On 6G?
| Telecom | Tech Giants | Academia | Others |
| Huawei (China) | Intel | University of California, Berkeley (USA) | Space X (USA) |
| Nokia (Finland) | Microsoft | Technical University of Munich (Germany) | OneWeb (UK) |
| Ericsson (Sweden) | Tsinghua University (China) | DRDO (India) | |
| Samsung (S.Korea) | Apple | IMDEA Networks Institute (Spain) | European Commission |
| Qualcomm (USA) | Reliance Jio | IIT Madras (India) | National Science Foundation |
Which One Do You Think Is The Best?
To summarize, while 5G is the catalyst for today’s connectivity revolution, 6G will shape the future, enabling an even more immersive, intelligent, and globally connected world.
While 5G has already begun transforming the mobile landscape with faster speeds, lower latency, and the ability to connect more devices, 6G promises to take connectivity even further. 6G will offer ultra-high speeds up to 100 times faster than 5G, near-zero latency, and more intelligent networks powered by AI and quantum technologies.






Leave a Reply